The Dangers of Gum Disease
“People think of gum disease in terms of their teeth, but they don’t think about the fact that gum disease is a serious infection that can release bacteria into the bloodstream” – Dr. Robert Genco, editor “Journal of Periodontology”
There are millions of germs that live in your mouth. If you suffer from gum disease, you have open wounds in your gums that allow these bacteria to enter directly into your bloodstream and circulate throughout your body. Research has shown that there is a direct correlation between periodontal disease and heart disease, respiratory disease, diabetes, kidney disease, head and neck cancer, and increased risk of preterm delivery.
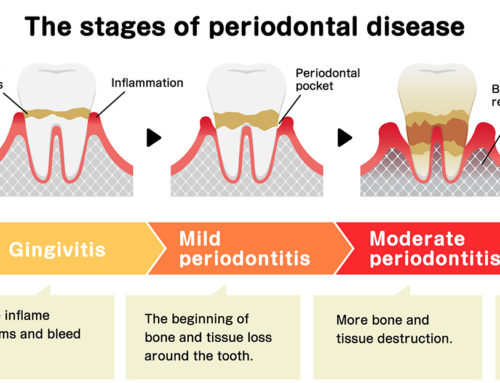
Gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss for the majority of adults. When an individual has gum disease it means that there is an active infection in your mouth.
What you need to know about Bisphosphonates. Bisphosphonates a.k.a. bone-sparing drugs, are used to treat and help prevent osteoporosis.